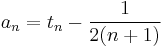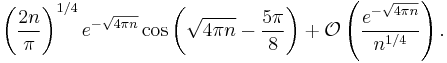Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing operator
- "GKW" redirects here. For the Indian engineering firm see Guest Keen Williams.
In mathematics, the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing operator, named after Carl Gauss, Rodion Osievich Kuzmin, and Eduard Wirsing, occurs in the study of continued fractions; it is also related to the Riemann zeta function.
Contents |
Introduction
The Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing operator is the transfer operator of the Gauss map
This operator acts on functions as
The zeroth eigenfunction of this operator is
which corresponds to an eigenvalue of 1. This eigenfunction gives the probability of the occurrence of a given integer in a continued fraction expansion, and is known as the Gauss–Kuzmin distribution. This follows in part because the Gauss map acts as a truncating shift operator for the continued fractions: if
is the continued fraction representation of a number 0 < x < 1, then
Additional eigenvalues can be computed numerically; the next eigenvalue is λ1 = −0.3036630029... (sequence A038517 in OEIS) and its absolute value is known as the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing constant. Analytic forms for additional eigenfunctions are not known. It is not known if the eigenvalues are irrational.
Relationship to the Riemann zeta
The GKW operator is related to the Riemann zeta function. Note that the zeta can be written as
which implies that
by change-of-variable.
Matrix elements
Consider the Taylor series expansions at x=1 for a function f(x) and ](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/c7e71a5c4930771c39153232e8ae894e.png) . That is, let
. That is, let
and write likewise for g(x). The expansion is made about x = 1 because the GKW operator is poorly-behaved at x = 0. The expansion is made about 1-x so that we can keep x a positive number, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. Then the GKW operator acts on the Taylor coefficients as
where the matrix elements of the GKW operator are given by
This operator is extremely well formed, and thus very numerically tractable. Note that each entry is a finite rational zeta series. The Gauss–Kuzmin constant is easily computed to high precision by numerically diagonalizing the upper-left n by n portion. There is no known closed-form expression that diagonalizes this operator; that is, there are no closed-form expressions known for the eigenvalues or eigenvectors.
Riemann zeta
The Riemann zeta can be written as
where the 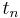 are given by the matrix elements above:
are given by the matrix elements above:
Performing the summations, one gets:
where 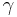 is the Euler–Mascheroni constant. These
is the Euler–Mascheroni constant. These 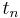 play the analog of the Stieltjes constants, but for the falling factorial expansion. By writing
play the analog of the Stieltjes constants, but for the falling factorial expansion. By writing
one gets: a0 = −0.0772156... and a1 = −0.00474863... and so on. The values get small quickly but are oscillatory. Some explicit sums on these values can be performed. They can be explicitly related to the Stieltjes constants by re-expressing the falling factorial as a polynomial with Stirling number coefficients, and then solving. More generally, the Riemann zeta can be re-expressed as an expansion in terms of Sheffer sequences of polynomials.
This expansion of the Riemann zeta is investigated in [1][2][3][4][5] The coefficients are decreasing as
References
- ^ A. Yu. Eremin, I. E. Kaporin, and M. K. Kerimov, "The calculation of the Riemann zeta-function in the complex domain", U.S.S.R. Comput. Math. and Math. Phys. 25 (1985), no. 2, 111–119
- ^ A. Yu. Yeremin, I. E. Kaporin, and M. K. Kerimov, "Computation of the derivatives of the Riemann zeta-function in the complex domain", U.S.S.R. Comput. Math. and Math. Phys. 28 (1988), no. 4, 115–124
- ^ Luis Báez-Duarte, "A New Necessary and Sufficient Condition for the Riemann Hypothesis" (2003) ArXiv math.NT/0307215
- ^ Luis Báez-Duarte, "A sequential Riesz-like criterion for the Riemann hypothesis", Internation Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences, 21, pp. 3527–3537 (2005)
- ^ Philippe Flajolet and Linas Vepstas, "On differences of zeta values", J. Comput. Appl. Math. 220, No. 1-2, 58-73 (2008).
General references
- A. Ya. Khinchin, Continued Fractions, 1935, English translation University of Chicago Press, 1961 ISBN 0-486-69630-8 (See section 15).
- K. I. Babenko, On a Problem of Gauss, Soviet Mathematical Doklady 19:136–140 (1978) MR 57 #12436
- K. I. Babenko and S. P. Jur'ev, On the Discretization of a Problem of Gauss, Soviet Mathematical Doklady 19:731–735 (1978). MR 81h:65015
- A. Durner, On a Theorem of Gauss–Kuzmin–Lévy. Arch. Math. 58, 251–256, (1992). MR 93c:11056
- A. J. MacLeod, High-Accuracy Numerical Values of the Gauss–Kuzmin Continued Fraction Problem. Computers Math. Appl. 26, 37–44, (1993).
- E. Wirsing, On the Theorem of Gauss–Kuzmin–Lévy and a Frobenius-Type Theorem for Function Spaces. Acta Arith. 24, 507–528, (1974). MR 49 #2637
Further reading
- Keith Briggs, A precise computation of the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing constant (2003) (Contains a very extensive collection of references.)
- Phillipe Flajolet and Brigitte Vallée, On the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing Constant (1995).
- Linas Vepstas The Bernoulli Operator, the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing Operator, and the Riemann Zeta (2004) (PDF)
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Gauss-Kuzmin-Wirsing Constant" from MathWorld.
- Sloane's A038517 . The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
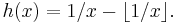
 = \sum_{n=1}^\infty \frac {1}{(x%2Bn)^2} f \left(\frac {1}{x%2Bn}\right).](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/094d61119473a3dc1587af76fcbbe470.png)
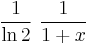
![x=[0;a_1,a_2,a_3,\dots]\,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/3d2b2f8262a6671a53de022c8d0ae613.png)
![h(x)=[0;a_2,a_3,\dots].\,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cee0a342002d3556192dbdbb36bb224b.png)
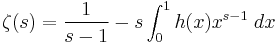
![\zeta(s)=\frac{s}{s-1}-s\int_0^1 x \left[Gx^{s-1} \right]\, dx](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/2107488f1e720ac425ec7cd9ea4f8e5f.png)
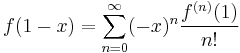
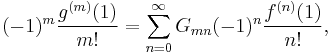
![G_{mn}=\sum_{k=0}^n (-1)^k {n \choose k} {k%2Bm%2B1 \choose m} \left[ \zeta (k%2Bm%2B2)- 1\right].](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/e69af77408134032391227bb882e0d6e.png)
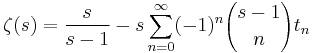
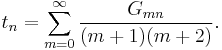
![t_n=1-\gamma %2B \sum_{k=1}^n (-1)^n {n \choose k} \left[ \frac{1}{k} %2B \frac {\zeta(k%2B1)} {k%2B1} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/34d7f70088ede89aca2b30982fe25322.png)